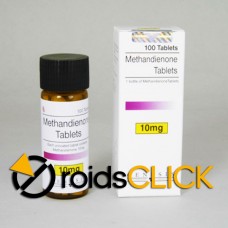
Methandienone tablets (D-Bol)
Methandienone tablets (D-Bol)
10mg/tab (100 tablets)
Metandienone (INN) (brand names Averbol, Dianabol, Danabol, Metanabol, Naposim, Vetanabol), or methandienone (BAN), also known as methandrostenolone, as well as 17α-methyl-δ1-testosterone or as 17α-methylandrost-1,4-dien-17β-ol-3-one, is an orally active, synthetic anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) and a 17α-methylated derivative of testosterone (specifically, the 17α-methylated derivative of boldenone (Δ1-testosterone)).
Metandienone was originally developed in 1957 by CIBA and marketed in Germany and the United States. As the CIBA product Dianabol, metandienone quickly became the first widely used anabolic-androgenic steroid among professional and amateur athletes, and remains the most common orally-administered steroid for non-medical use.
It is currently a controlled substance in the U.S.and UK and remains popular among bodybuilders. Metandienone is readily available without a prescription in certain countries, and is also manufactured in Asia and many Eastern European countries.
It is used by bodybuilders and metandienone continues to be used to this day, typically being combined (stacked) with injectable compounds, such as testosterone propionate, enanthate, cypionate as well as other injectable drugs like trenbolone acetate.
Several successful athletes and professional bodybuilders have admitted long-term metandienone use before the drug was banned, including Arnold Schwarzenegger.Other steroids stacked with metandienone are primarily, if not always, injectable compounds such as testosterone, trenbolone and nandrolone. Large doses and long-term use of metandienone have been associated with eccentric left ventricular hypertrophy which presents substantially increased risks of cardiomyopathy if and when the hypertrophy atrophies. Athleticism is typically associated with left-ventricular hypertrophy; however, natural athleticism generally presents concentric left ventricular growth which is not linked to an increased risk of cardiomyopathy.